The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), agreed to by all 191 United Nations Member States at the Millennium Summit in 2000, set specific targets for reducing poverty, hunger, disease, illiteracy, environmental degradation and discrimination against women by 2015. Below is an illustration summarising the progress of the basin states towards the MDGs at the beginning of 2012.
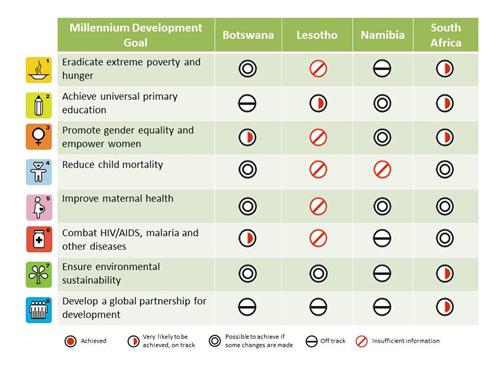
( click to enlarge )
A summary of the Millennium Develop Goals is provided in the box below.
Box: Millennium Development Goals
Goal 1: Halve extreme poverty and hunger
-
Halve, between 1990 and 2015, the proportion of people whose income is less than one dollar a day.
-
Achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all, including women and young people.
-
Halve, between 1990 and 2015, the proportion of people who suffer from hunger.
Goal 2: Achieve universal primary education
-
Ensure that, by 2015, children everywhere, boys and girls alike, will be able to complete a full course of primary schooling.
Goal 3: Promote gender quality and empower women
Goal 4: Reduce child mortality
Goal 5: Improve maternal health
-
Reduce by three-quarters, between 1990 and 2015, the maternal mortality ratio.
-
Achieve, by 2015, universal access to reproductive health.
Goal 6: Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases
Goal 7: Ensure environmental sustainability
-
Integrate the principles of sustainable development into country policies and programmes and reverse the loss of environmental resources.
-
Reduce biodiversity loss, achieving, by 2010, a significant reduction in the rate of loss.
-
Halve, by 2015, the proportion of people without sustainable access to safe drinking water and adequate sanitation.
-
By 2020, to have achieved a significant improvement in the lives of at least 100 million slum dwellers.
Goal 8: Develop a Global Partnership for Development
-
Develop further an open, rule-based, predictable, non-discriminatory trading and financial system.
-
Address the special needs of the Least Developed Countries, landlocked countries and small island developing states.
-
Deal comprehensively with developing countries’ debt.
-
In cooperation with developing countries, develop and implement strategies for decent and productive work for youth.
-
In cooperation with pharmaceutical companies, provide access to affordable, essential drugs in developing countries.
-
In cooperation with the private sector, make available the benefits of new technologies, especially information and communications technologies.
Source: United Nations 2008
